NASA Tech to Use Moonlight to Enhance Measurements from Space
NASA Tech to Use Moonlight to Enhance Measurements from Space
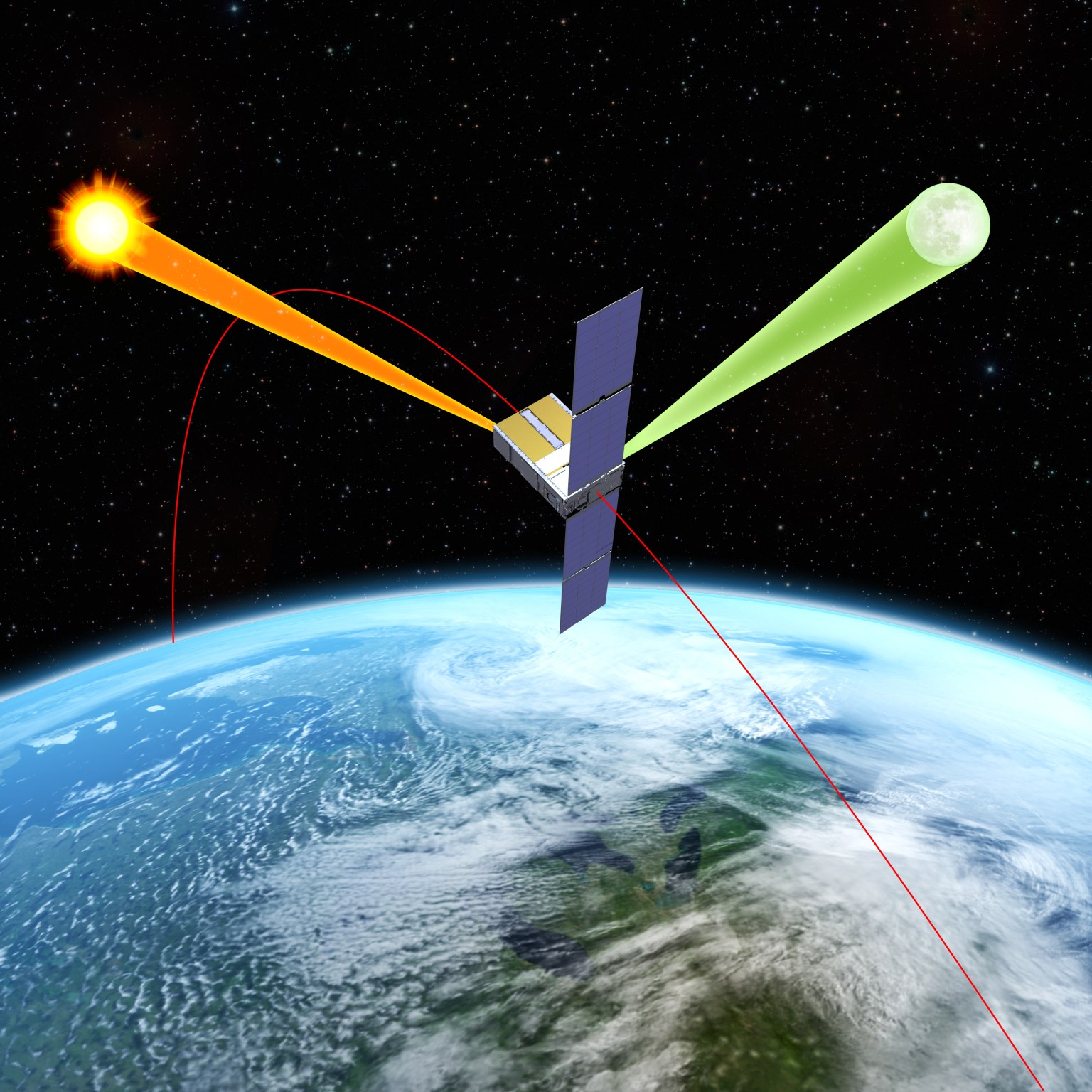
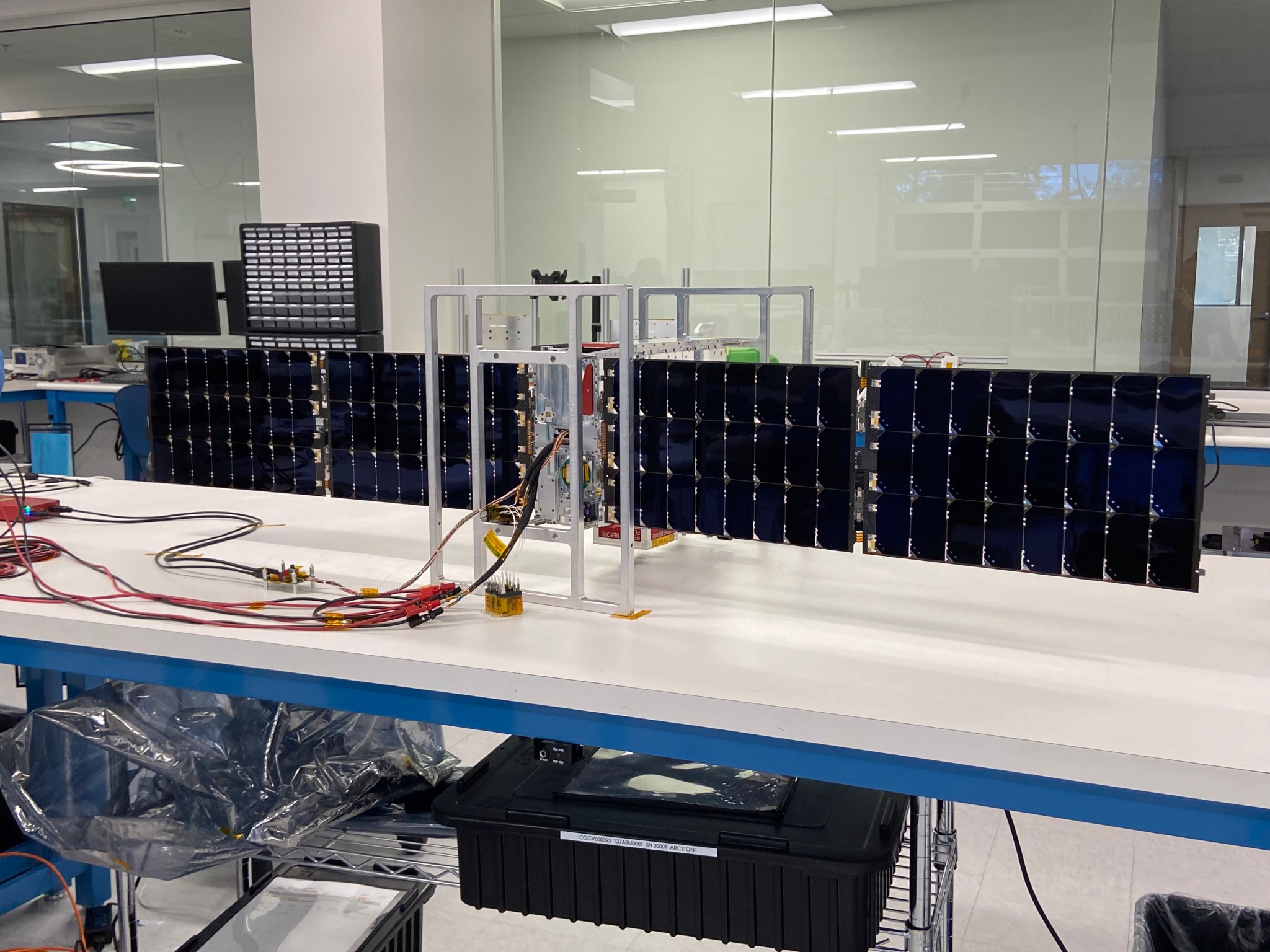
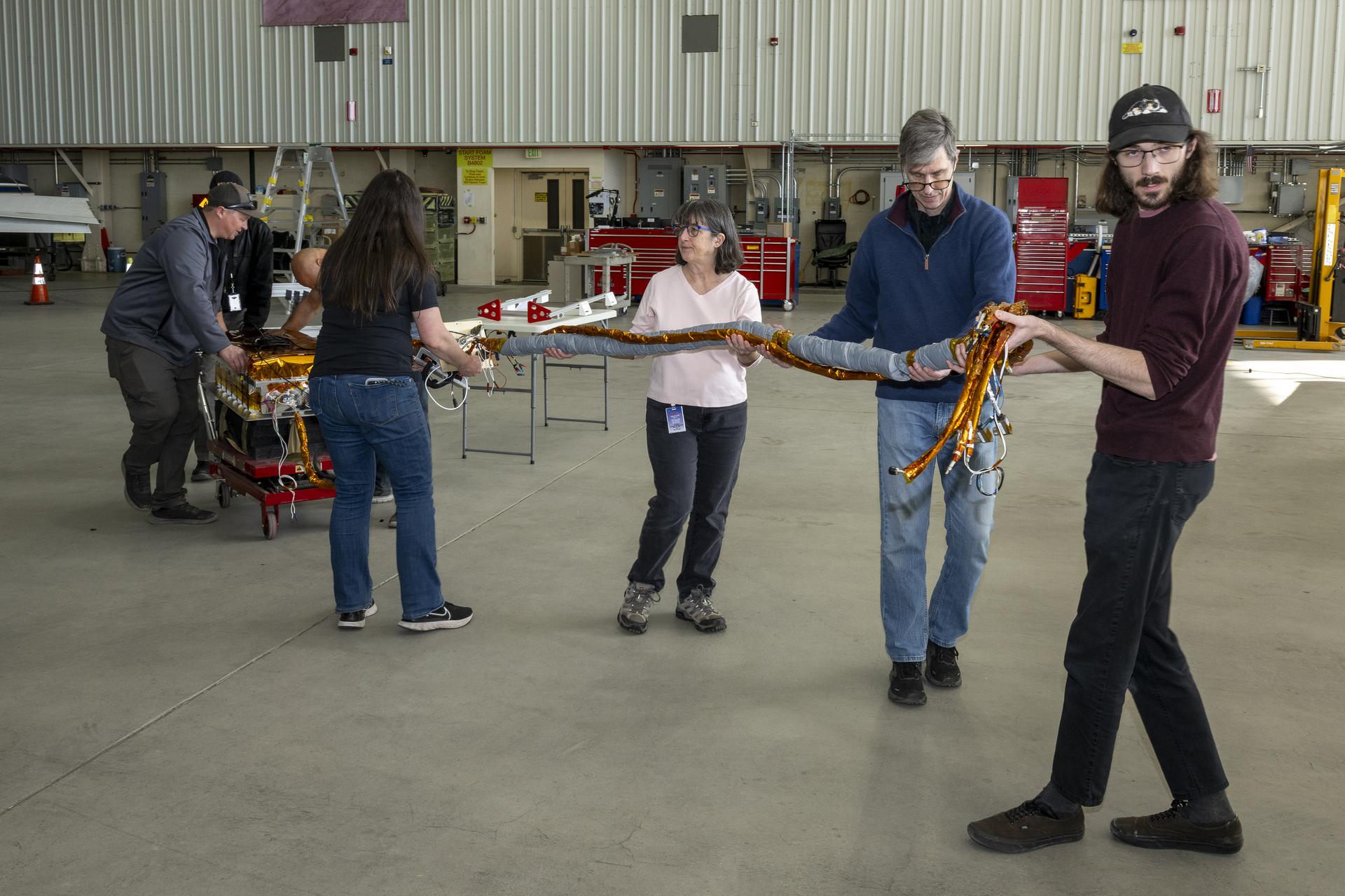
NASA will soon launch a one-of-a-kind instrument, called Arcstone, to improve the quality of data from Earth-viewing sensors in orbit. In this technology demonstration, the mission will measure sunlight reflected from the Moon— a technique called lunar calibration. Such measurements of lunar spectral reflectance can ultimately be used to set a high-accuracy, universal standard for use across the international scientific community and commercial space industry.
To ensure satellite and airborne sensors are working properly, researchers calibrate them by comparing the sensor measurements against a known standard measurement. Arcstone will be the first mission exclusively dedicated to measuring lunar reflectance from space as a way to calibrate and improve science data collected by Earth-viewing, in-orbit instruments.
“One of the most challenging tasks in remote sensing from space is achieving required instrument calibration accuracy on-orbit,” said Constantine Lukashin, principal investigator for the Arcstone mission and physical scientist at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. “The Moon is an excellent and available calibration source beyond Earth’s atmosphere. The light reflected off the Moon is extremely stable and measurable at a very high level of detail. Arcstone’s goal is to improve the accuracy of lunar calibration to increase the quality of spaceborne remote sensing data products for generations to come.”
Across its planned six-month mission, Arcstone will use a spectrometer — a scientific instrument that measures and analyzes light by separating it into its constituent wavelengths, or spectrum — to measure lunar spectral reflectance. Expected to launch in late June as a rideshare on a small CubeSat, Arcstone will begin collecting data, a milestone called first light, approximately three weeks after reaching orbit.
“The mission demonstrates a new, more cost-efficient instrument design, hardware performance, operations, and data processing to achieve high-accuracy reference measurements of lunar spectral reflectance,” said Lukashin.
Measurements of lunar reflectance taken from Earth’s surface can be affected by interference from the atmosphere, which can complicate calibration efforts. Researchers already use the Sun and Moon to calibrate spaceborne instruments, but not at a level of precision and agreement that could come from having a universal standard.
Lukashin and colleagues want to increase calibration accuracy by getting above the atmosphere to measure reflected solar wavelengths in a way that provides a stable and universal calibration source. Another recent NASA mission, called the Airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance mission also used sensors mounted on high-altitude aircraft to improve lunar irradiance measurements from planes.
There is not an internationally accepted standard (SI-traceable) calibration for lunar reflectance from space across the scientific community or the commercial space industry.
“Dedicated radiometric characterization measurements of the Moon have never been acquired from a space-based platform,” said Thomas Stone, co-investigator for Arcstone and scientist at the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). “A high-accuracy, SI-traceable lunar calibration system enables several important capabilities for space-based Earth observing missions such as calibrating datasets against a common reference – the Moon, calibrating sensors on-orbit, and the ability to bridge gaps in past datasets.”
If the initial Arcstone technology demonstration is successful, a longer Arcstone mission could allow scientists to make the Moon the preferred reference standard for many other satellites. The new calibration standard could also be applied retroactively to previous Earth data records to improve their accuracy or fill in data gaps for data fields. It could also improve high-precision sensor performance on-orbit, which is critical for calibrating instruments that may be sensitive to degradation or hardware breakdown over time in space.
“Earth observations from space play a critical role in monitoring the environmental health of our planet,” said Stone. “Lunar calibration is a robust and cost-effective way to achieve high accuracy and inter-consistency of Earth observation datasets, enabling more accurate assessments of Earth’s current state and more reliable predictions of future trends.”
The Arcstone technology demonstration project is funded by NASA’s Earth Science Technology Office’s In-space Validation of Earth Science Technologies. Arcstone is led by NASA’s Langley Research Center in partnership with Colorado University Boulder’s Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, USGS, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Resonon Inc., Blue Canyon Technologies, and Quartus Engineering.
For more information on NASA’s Arcstone mission visit:
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0